The geometric average return answers the question – The geometric average return, a crucial concept in investment analysis, provides a comprehensive understanding of portfolio performance over time. Unlike the arithmetic average, which can be distorted by extreme values, the geometric average accurately captures the true growth rate of an investment, making it an indispensable tool for informed decision-making.
This in-depth exploration will delve into the significance, applications, and limitations of the geometric average return, empowering investors with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of financial markets.
Geometric Average Return Overview
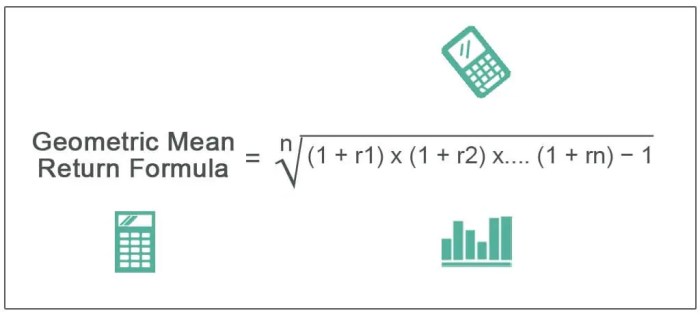
The geometric average return (GAR) is a statistical measure that calculates the average return of an investment over a specific period, accounting for the compounding effect. It is distinct from the arithmetic average return, which simply averages the returns over the period.
GAR is significant in investment analysis as it provides a more accurate representation of the actual growth of an investment. This is because it considers the reinvestment of earnings, which can have a substantial impact on the overall return.
Example of Calculating Geometric Average Return
Consider an investment that returns 10% in the first year, 5% in the second year, and 15% in the third year. The arithmetic average return is (10% + 5% + 15%) / 3 = 10%. However, the geometric average return is calculated as (1 + 0.10) – (1 + 0.05) – (1 + 0.15) – 1 = 10.62%.
Applications of Geometric Average Return
Measuring Investment Performance
GAR is used to measure the performance of investments, such as mutual funds or stocks. It provides a more accurate assessment of the investment’s growth over time, especially when there are significant fluctuations in returns.
Risk-Adjusted Return Calculations
GAR is also used in risk-adjusted return calculations, such as the Sharpe ratio and the Sortino ratio. These ratios compare the return of an investment to its risk, and GAR is used to calculate the expected return over a given period.
Portfolio Optimization
GAR is used in portfolio optimization to maximize returns while minimizing risk. By using GAR to calculate the expected return of different assets, investors can create portfolios that meet their specific risk and return objectives.
Comparison with Arithmetic Average Return
Advantages and Disadvantages of Geometric Average Return
GAR has several advantages over the arithmetic average return. It considers the compounding effect, which provides a more accurate representation of investment growth. It is also less sensitive to outliers and extreme returns.
However, GAR can be less intuitive than the arithmetic average return and may not be appropriate in all situations. For example, it is not suitable for calculating the average return of a series of independent events.
Examples of Differences between Geometric and Arithmetic Average Returns
Consider two investments, one that returns 10% each year and another that returns 5% in the first year and 15% in the second year. The arithmetic average return is 10% for both investments, but the geometric average return is 10% for the first investment and 10.62% for the second investment.
Limitations of Geometric Average Return
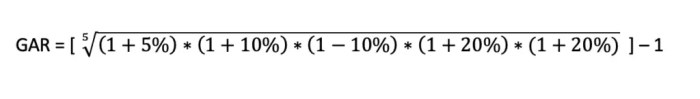
When Geometric Average Return May Not Be Appropriate
GAR may not be an appropriate measure in certain situations. For example, it is not suitable for calculating the average return of a series of independent events, such as the returns of a lottery or a series of coin flips.
Examples of Situations Where Other Measures May Be More Suitable
In some cases, other measures of average return may be more suitable. For example, the arithmetic average return may be more appropriate for calculating the average return of a series of independent events.
Advanced Applications of Geometric Average Return: The Geometric Average Return Answers The Question
Stochastic Processes
GAR is used in stochastic processes to model the growth of investments. These models consider the random nature of investment returns and use GAR to calculate the expected growth rate.
Financial Modeling, The geometric average return answers the question
GAR is used in financial modeling to simulate the performance of investments and portfolios. These models use GAR to calculate the expected returns and risks of different investment strategies.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the key difference between geometric and arithmetic average returns?
The geometric average considers the compounding effect of returns, while the arithmetic average does not, leading to a more accurate representation of actual investment growth.
When is the geometric average return more appropriate than the arithmetic average return?
The geometric average is more suitable when dealing with long-term investment horizons or when returns are volatile, as it provides a more realistic assessment of the true growth rate.