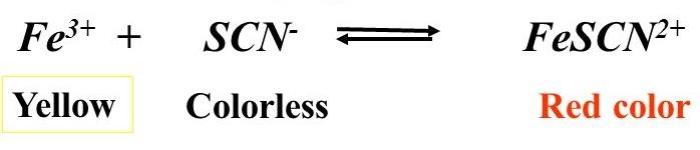Colorimetric determination of an equilibrium constant in aqueous solution – Colorimetric determination of equilibrium constants in aqueous solutions plays a pivotal role in understanding the behavior of chemical reactions and processes. This technique utilizes the principles of spectrophotometry to quantify the concentration of a substance based on its absorbance of light at a specific wavelength.
Through the Beer-Lambert Law, a linear relationship is established between absorbance and concentration, allowing for the determination of equilibrium constants. The experimental setup involves preparing solutions, reagents, and instrumentation, followed by data collection and analysis.
Introduction

Colorimetric determination is a technique that utilizes the relationship between the concentration of a substance and the intensity of the color it produces. This technique is widely applied in the analysis of equilibrium constants in aqueous solutions.
An equilibrium constant is a quantitative measure of the extent to which a chemical reaction proceeds towards completion. It provides valuable insights into the spontaneity and direction of reactions in aqueous solutions.
Spectrophotometric Techniques
Spectrophotometry is a technique that measures the absorption or emission of light by a sample. In colorimetric determination, spectrophotometry is used to quantify the concentration of a substance based on the intensity of the colored species it forms.
The Beer-Lambert Law states that the absorbance of a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species and the path length of the light beam through the solution. This law is crucial for determining equilibrium constants using colorimetric methods.
The calibration curve method is a technique used to determine the equilibrium constant. A series of solutions with known concentrations of the reactants are prepared, and the absorbance of each solution is measured. A calibration curve is then constructed by plotting the absorbance against the concentration of the reactants.
Experimental Setup and Procedures, Colorimetric determination of an equilibrium constant in aqueous solution
The experimental setup for colorimetric determination of equilibrium constants typically involves:
- Preparation of solutions: Solutions of the reactants and reagents are prepared at known concentrations.
- Instrumentation: A spectrophotometer is used to measure the absorbance of the solutions.
- Data collection: The absorbance of each solution is measured at a specific wavelength.
- Data analysis: The data is analyzed using the Beer-Lambert Law and the calibration curve method to determine the equilibrium constant.
Essential Questionnaire: Colorimetric Determination Of An Equilibrium Constant In Aqueous Solution
What is the principle behind colorimetric determination of equilibrium constants?
Colorimetric determination relies on the Beer-Lambert Law, which establishes a linear relationship between the absorbance of light and the concentration of a substance in solution.
How is the equilibrium constant determined using this technique?
The equilibrium constant is calculated from the absorbance measurements at different concentrations using the Beer-Lambert Law and the calibration curve method.
What factors can affect the accuracy of the equilibrium constant determination?
Factors such as temperature, pH, and ionic strength can influence the equilibrium constant value. Careful control of these factors is essential for accurate determination.