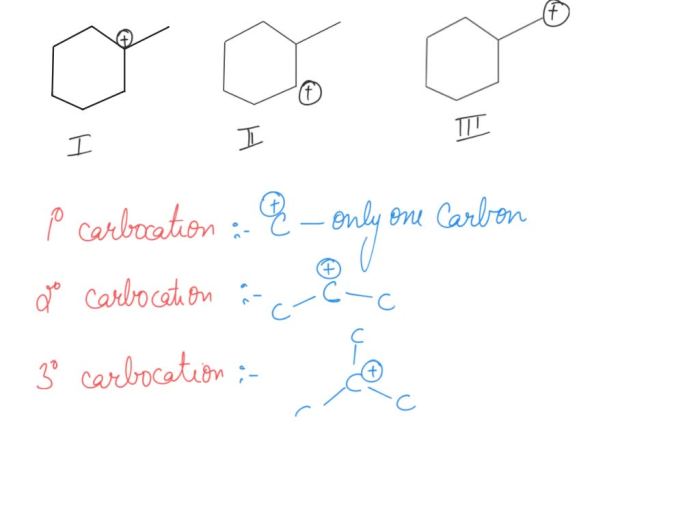
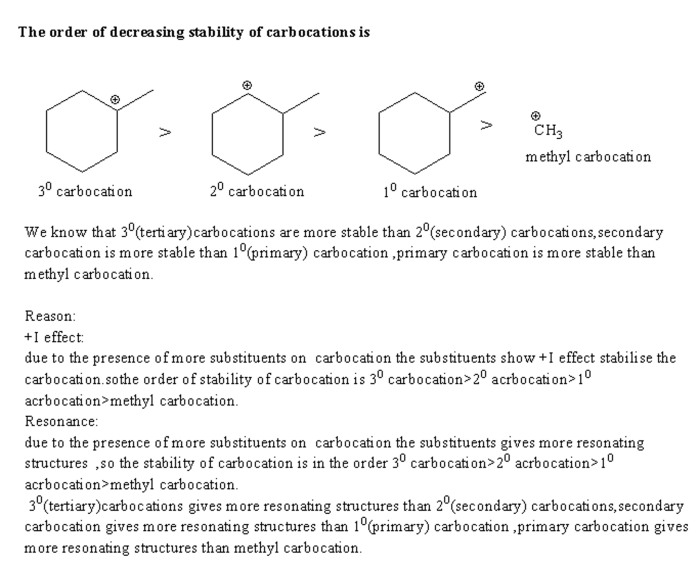
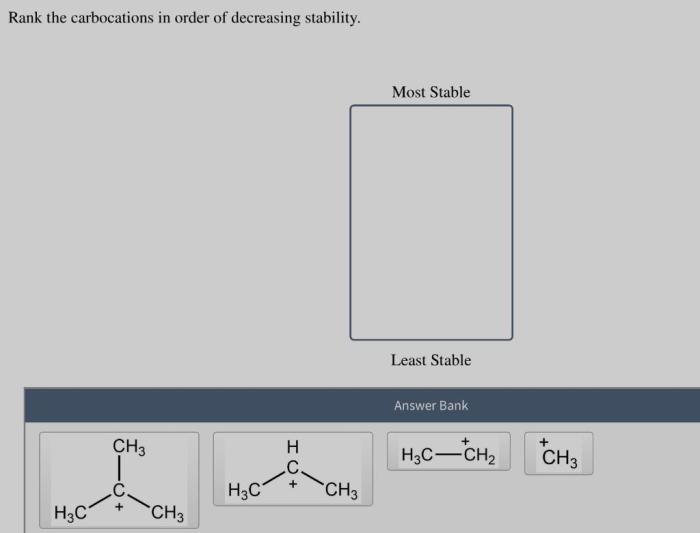
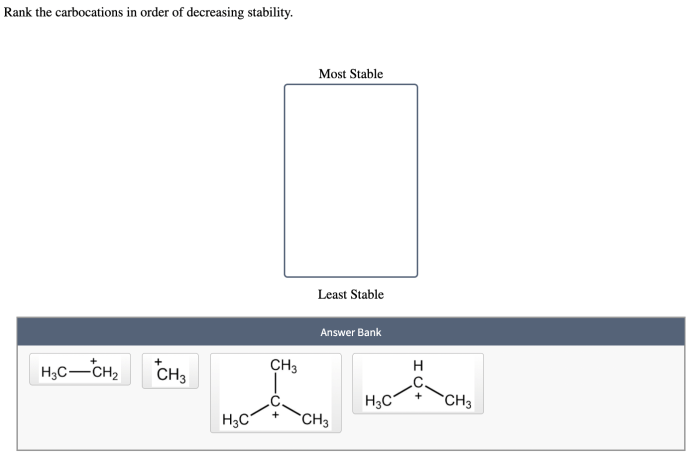
Rank the carbocations in order of decreasing stability – Carbocation stability plays a crucial role in understanding organic reaction mechanisms. This article delves into the factors that influence carbocation stability and presents methods for ranking them in order of decreasing stability.
Factors such as electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups, resonance, and steric effects are examined in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of carbocation stability.
2. Factors Affecting Carbocation Stability: Rank The Carbocations In Order Of Decreasing Stability
Carbocation stability is influenced by various factors, including:
- Electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups:Electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) decrease carbocation stability by withdrawing electrons from the carbocation center. Conversely, electron-donating groups (EDGs) increase carbocation stability by donating electrons to the carbocation center.
- Resonance and hyperconjugation:Resonance and hyperconjugation stabilize carbocations by delocalizing the positive charge over multiple atoms. This dispersal of charge reduces the electron deficiency at the carbocation center, making it more stable.
- Inductive effects:Inductive effects can either stabilize or destabilize carbocations depending on the nature of the substituents. Inductive electron-withdrawing groups (IEWGs) destabilize carbocations, while inductive electron-donating groups (IEDGs) stabilize carbocations.
- Steric effects:Steric effects can destabilize carbocations by hindering the approach of nucleophiles to the carbocation center. This hindrance reduces the reactivity of the carbocation, making it less stable.
Clarifying Questions
What are the primary factors that affect carbocation stability?
Electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups, resonance, hyperconjugation, inductive effects, and steric effects are the key factors that influence carbocation stability.
How can carbocations be ranked in order of decreasing stability?
Carbocations can be ranked based on their stability using resonance theory, molecular orbital theory, frontier molecular orbital theory, and density functional theory.